
Summary:
Being knowledgeable about the different financial ratios puts us ahead of a lot of other investors.
Financial ratios assist in reaching fact-based judgments about a company's health.
Use these eight crucial financial parameters to get a clear sense of a company's future.
The numbers tell the story and that advice still holds true whether we are thinking about establishing a business, investing in one, or already own one.
Our financial statements serve as a benchmark for success in business, much as our report card does in education. Understanding how to interpret financial statements and make fact-based decisions about a company's viability are essential skills for anyone hoping to succeed in business.
There are many levels of sophistication when it comes to reading a financial statement. We should be able to comprehend our cash flow as well as the relationships between our income, expenses, assets, and obligations as a starting point.
However, in order to become a knowledgeable business owner and investor, we must broaden our knowledge and grasp even more complex financial principles in order to assess the viability of our company or one in which we intend to invest.
Our Personal Financial Statement
Ensure to master our personal financial statement by understand the 8 essential world of a financial statement.
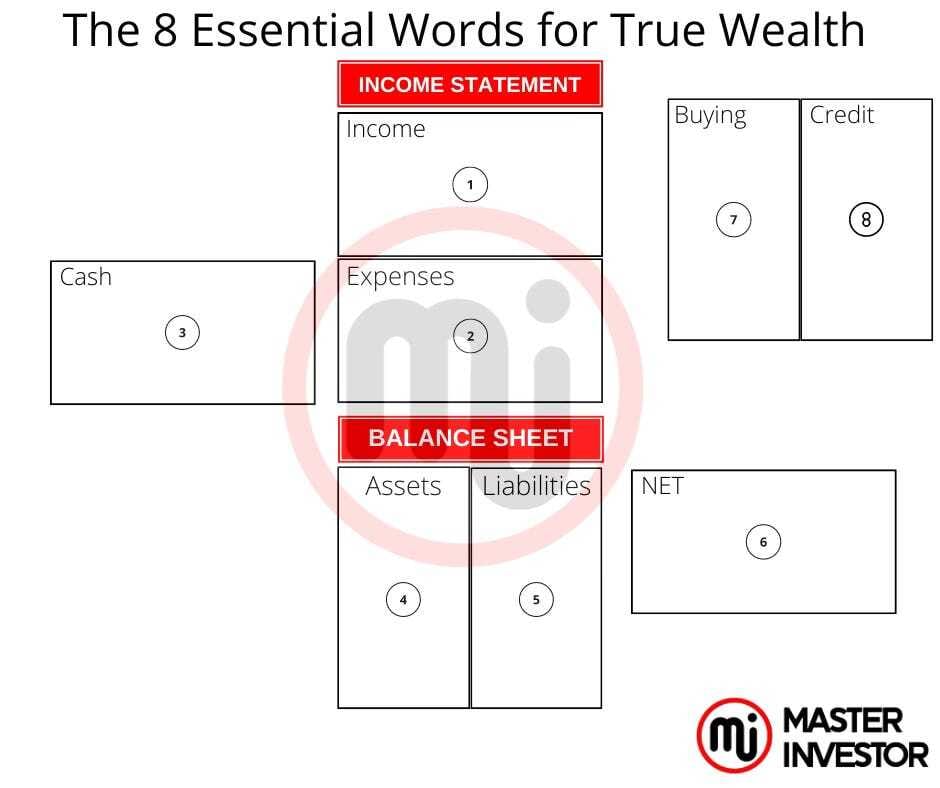
Our personal financial statement is composed of 6 important words.
1- Income
2- Expenses
3- Assets
4- Liabilities
5-Cash
6-Flow
Then, we must understand the Net of our personal financial statement to see when’re we are financial today in regards to our wealth. Then we will find out our Buying power and Credit leverage. As we can see in the diagram above, we must have to master the relationship between the income statement and balance sheet. Keep ihn mid that a business or investment financial statement also looks like the one above.
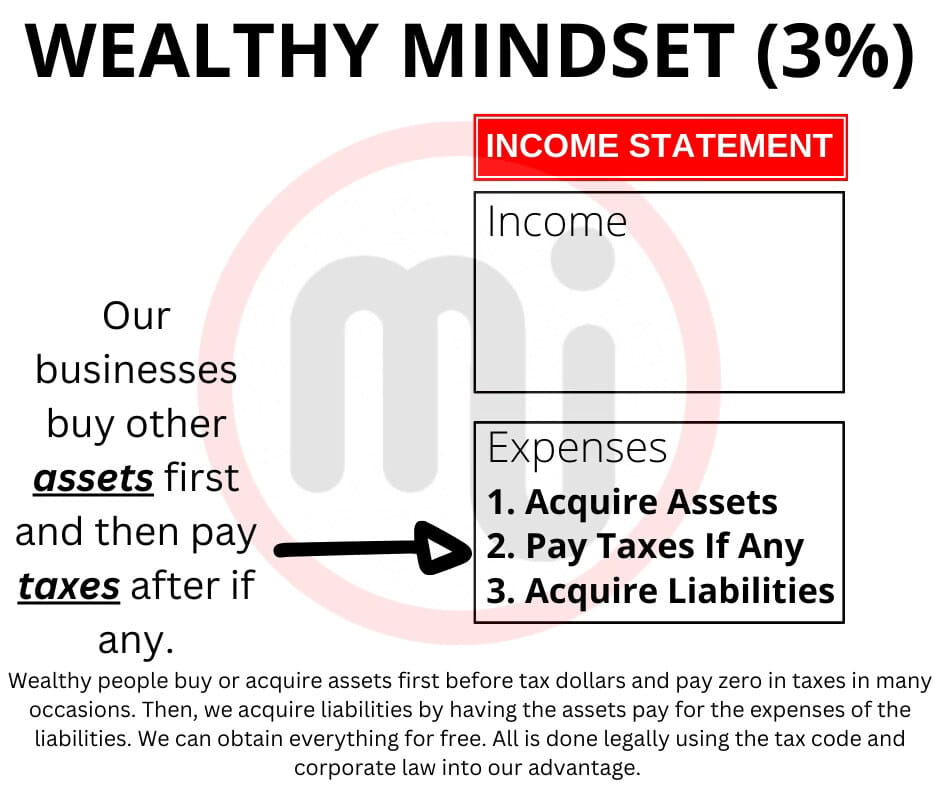
Once we master and improve our financial statements, then we can improve a company’s financial statement. Go with rule #1 of our community here at masterinvestor, which is that we work to build passive income and make money multiple through sound investing.
We will be financial free and building true wealth when our financial statements look like this:
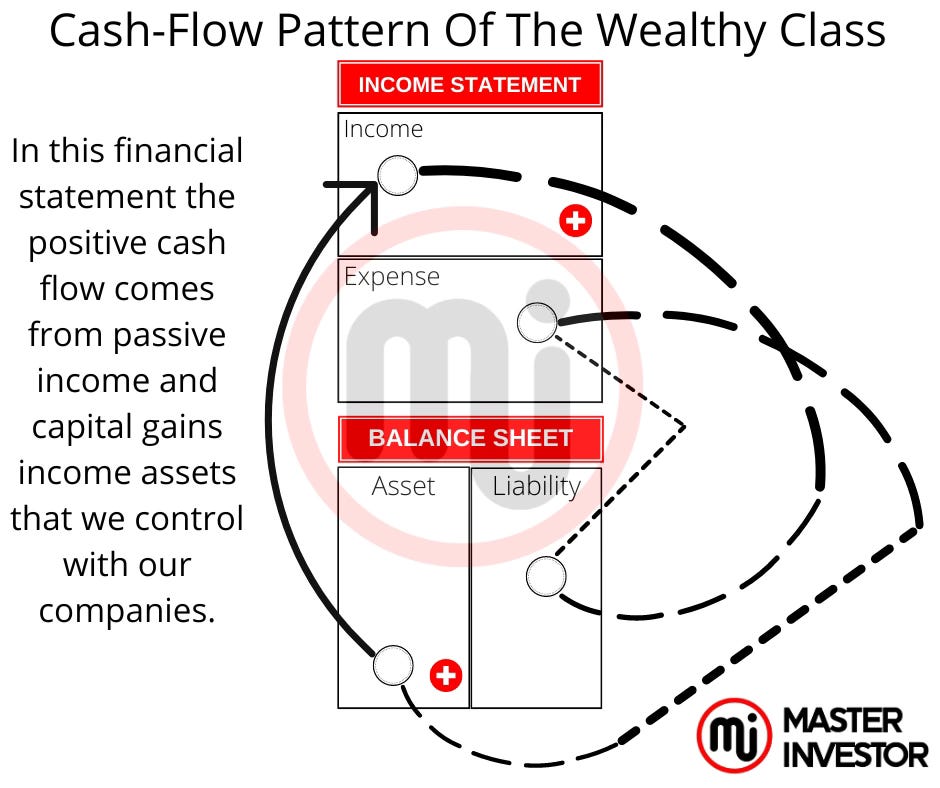
In other words, we have to make investing for passive income a priority and have financial education in our daily training to build wealth. Take a look at the next diagram where it shows that our main expenses are investing in passive income assets and invest in financial eduction daily.
Which financial ratios are important?
There are important ratios that you may use to assess a company's financial health in order to comprehend its overall health.
"Key ratios take data from the subject company's financial statements, such as the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows," according to Investopedia. These statements' contents are compared to one another to create ratios that show important facets of the business's financial picture, including debt utilization, liquidity, profitability, and earnings strength.
Although calculating these important ratios is not difficult, many individuals are unaware of them. We have already outperformed many investors in our ability to assess a company's health just by reading this piece.
Here are eight essential financial measures that we should be aware of.
Financial Ratio #1: percentage of gross margin
Compute: Sales / Gross Margin = Gross Margin Percentage
Sales less the cost of goods sold is the gross margin. Therefore, our gross margin is $25 if we sell $100 worth of bananas and they cost us $75.
The proportion of sales that remain after deducting the cost of the goods sold is known as the gross margin percentage, which is calculated by dividing the gross margin by sales.
In this case, the gross margin percentage would be.25, or 25%, or $25/$100.
Why is the percentage of gross margin significant?
There won't be a net if the gross isn't there. For example, if we are investing in a company that is losing money despite having a high gross margin %, we can investigate whether the company is just being mishandled. Once everything is fixed, cleaning up the operations could result in a very profitable company.
How a business is set up and the various expenses it must cover determine how high the gross margin percentage should be.
For example, convenience stores still need to pay their clerks, utilities, taxes, rent, and a host of other expenditures after figuring out their gross margin %. They also needed to have enough leftover to provide the business owner and inside investor with a healthy return on his first investment.
It's feasible that we may afford to sell and turn a profit with a smaller gross margin percentage if we run an online business today because there is less chance of excessive expenses. However, in any firm, a larger gross margin is preferable.
Financial Ratio #2: percentage of net operating margin
Net operating margin percentage is calculated as follows: EBIT / sales.
This ratio indicates the net profitability of a company's activities before deducting costs such as taxes and other uncontrollable expenses from the owner.
Sales less all operating expenses excluding capital costs like as interest, taxes, and dividends is our earnings before interest and taxes, or EBIT.
It offers us an idea of how well a firm is being handled and accounts for costs that are under our control. An extremely volatile EBIT may be a sign of a hazardous company. A steady one can be a sign of one that is predictable and well-managed.
How come net operating margin matters?
The net operating margin percentage is the ratio of EBIT to sales. Generally speaking, companies with higher net operating margin percentages are more robust than those with lower percentages. Better still, the higher!

Financial Ratio #3: operating leverage
Operational leverage is calculated as contribution / fixed expenses.
All businesses need to include fixed costs in their total cost structure. "Operating leverage" is the ratio of fixed costs to total expenses, which is computed by dividing contribution by fixed costs. Contribution is defined as gross margin (sales less cost of goods sold) less variable costs (all other costs not related to fixed costs that change with sales).
Examples of fixed costs include labor associated with full-time staff and the majority of facility-related expenses. Most people refer to this as overhead.
What makes operating leverage crucial?
A company with an operating leverage of one is making just enough money to cover its fixed expenses. This would imply that the owners receive no compensation. Any value greater than one indicates a profit. Once more, higher is preferable.
It can be worthwhile to investigate whether an under leveraged operating margin exists in a business with low operating leverage. A larger operating leverage could result from raising the gross margin through actions like raising prices.
Financial Ratio #4: Leverage
Financial leverage is calculated as follows: total capital used / shareholder equityFor most businesses to function, borrowing money is a need.
One important financial measure that indicates how much a company uses borrowed funds is financial leverage. The accounting value of all interest-bearing debt plus all owners' equity is known as total capital employed.
Therefore, our financial leverage would be two (i.e., $100,000 divided by $50,000) if we have $50,000 in debt and $50,000 in shareholder stock.
Why is financial leverage significant?
Similar to life, we don't want a firm to have too much debt. A company is riskier the more financial leverage it has because there is more debt that needs to be paid back.
That being stated, the parameters for what constitutes a sound financial leverage vary depending on the sort of organization. The entire picture of financial health is heavily influenced by other variables, including cash flow and cost of debt.
Financial Ratio #5: Total leverage
Calculation: operating leverage times financial leverage equals total leverage.
The operating leverage (key ratio #3) and financial leverage (key ratio #4) are multiplied to get the total leverage. As the company's owner, we are insiders and thus have some control over the overall leverage of the organization.
Why does total leverage matter?
The overall amount of risk that a business has in its current operations is represented by total leverage. Total leverage indicates the overall effect on equity owners that a specific business change should have.
Total leverage on the stock market might assist us in determining whether or not to invest in a company.
A well-managed American corporation typically maintains a total leverage ratio of less than five.
Financial Ratio #6: Debt-to-equity ratio
Debt-to-equity ratio calculation: total liabilities / total equity
This one should go without saying. It is a measurement of how much of the entire business (total liabilities) is funded by outsiders compared to how much is funded by insiders (total equity). Most companies aim to maintain a ratio of one to one or less.
Why is the ratio of debt to equity significant?
In general, a company's financial structure is more conservative the lower its debt-to-equity ratio. There is less danger in a corporation with a more conservative financial structure. We will have to assess our personal level of risk because an investor may not always be searching for less risk.
We can determine whether a possible investment is reaching or exceeding that acceptable risk level with the use of this essential ratio.
Financial Ratio #7: Quick and current ratios
Quick ratio is calculated as liquid assets divided by current liabilities.
Current ratio can be calculated as follows: current assets / current liabilities.
The purpose of the quick and current ratios is to indicate to us whether the company has sufficient liquid assets to cover its liabilities for the upcoming year.
A fast ratio solely considers liquid assets. This includes assets like money, securities, and receivables. It does not account for items like inventories, which could take some time to liquidate in the case that obligations need to be paid off, in contrast to the current ratio.
Which ratios are appropriate to utilize will depend on the kind of firm you are examining. A company that has a history of high inventory turnover, for example, might be better off using a current ratio, whereas a company that transfers its goods slowly would benefit more from a quick ratio.
What makes current and fast ratios significant?
It is typically an indication of trouble ahead when a company's current obligations exceed its present assets. Conversely, it is more appropriate to have a current ratio and a quick ratio of at least two to one.
Financial Ratio #8: equity return
Many people rank return on equity as one of the most significant essential financial ratios. It lets us evaluate how profitable a business is for its investors in relation to alternative investments.
What makes return on equity crucial?
Making money is the main goal of both owning and investing in businesses. It is not worthwhile to invest our time in a business with a low return on equity. Return on equity is influenced by a variety of factors, so it's critical to use all of these statistics to identify potential hidden opportunities in a company. For example, a poorly run company may have many metrics that look terrible, but in the proper hands, they could represent a goldmine.
Although the ratios might seem difficult at first, we will be surprised at how fast we can pick up the skills necessary to examine a corporation. Running these ratios on our own after downloading the financial statements of publicly traded corporations is a pleasant activity. See what we can discover and learn how to locate the information we require.
Recall that these ratios represent the vocabulary of a seasoned investor. Through self-education and acquiring financial literacy, we too may acquire the ability to "speak in ratios."
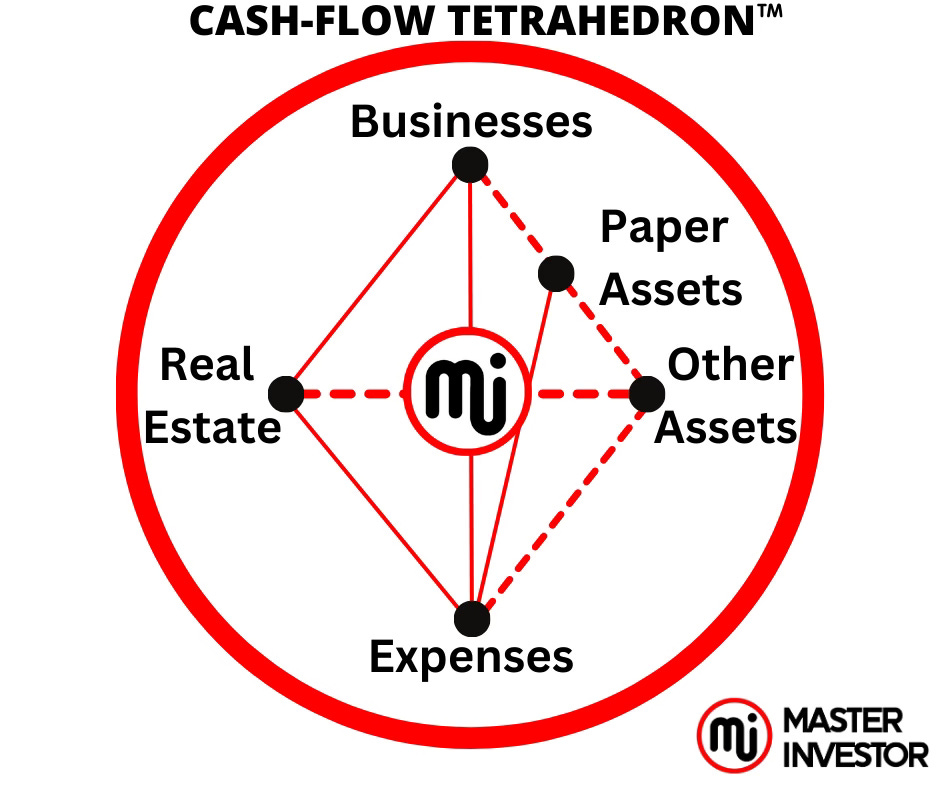
Choose The Side of The Cash Flow Circle That has Freedom to Be Wealthy

Now once we have chosen where we want to spend our time, then, we must get started by investing and getting new financial education. On the right side of the cash flow circle, we focus on budding passive income (positive cash flow) through businesses and investing. When we master to receive passive income, then automatically we will also get capital gains income from investments. Not all assets and asset classes bring passive income some will only bring in capital gains income. Focus on passive income and capital gains income will be easy to obtain.
Eventually our business will buy other businesses and investments that cash flow positively. When we achieve this then we have tap into the velocity of cash flow and infinite return on investment (money for noting). The best time to become wealthy is now because of the ability to access information and sell worldwide with systems.
Use the cash flow tetrahedron to reach infinite return on investment
Start investing in high quality financial education, by reading our financial eBooks:



Lucrative resources and tools:
Follow us on Instagram.
Listen to our Podcast.
Subscribe to our Newsletter.
Follow us on Tiktok.
Purchase a business digital Course.
Like our Facebook Page.
Join our Inner Circle.
I am reading: The 8 Financial Rations For A Business Owner
Comment, like, share and follow for more High Quality Financial Education Made Simple.

